Managing payroll can seem straightforward, until you start thinking about the records you need to keep. You might be wondering: What exactly counts as payroll records, and how long should I hold on to them? Payroll records include important details of employee compensation, such as gross wages, overtime, bonuses, tax withholdings, benefits administration, and deductions like social security and insurance contributions. Keeping these records precise ensures employees are paid correctly and on time while meeting labor, tax, and social security requirements in your region.
Managing payroll records also means securely storing data with strong confidentiality controls, regularly updating records to reflect employment or compensation changes, and having clear procedures to detect and fix errors. In this guide, we’ll break down what payroll records actually include, how to maintain them securely, and why they matter far more than just “paperwork.”
What are Payroll Records?
Payroll records, also known as payroll documentation, are detailed documents that track employee compensation and all related payment information. These documents include essential details such as pay rates, total earnings, hours worked, tax deductions, benefit contributions, bonuses, overtime, and other payments. Essentially, payroll records provide an official, accurate account of how each paycheck is calculated and paid.
These records are vital for ensuring fairness and accuracy in employee pay and play a crucial role in resolving any payment issues that may arise. Beyond internal use, payroll documentation supports compliance with legal and tax regulations, aids in preparing for audits, and helps businesses meet labor law requirements. Whether maintained as timesheets, payslips, or electronic summaries, payroll records form the backbone of transparent payroll management and help build trust between employers and employees.
Why Payroll Records are Important?
Payroll records may seem like just more paperwork, but behind those files lies the story of every paycheck, tax deduction, and every benefit you provide to your team. They’re the backbone of smooth business operations and fair employee relationships.
- Legal Compliance: Employers are required to keep accurate payroll records to ensure correct tax payments and adherence to labor regulations. Failure to maintain proper records can lead to severe fines and legal actions that may damage a company’s reputation and finances.
- Audit Readiness: Properly organized payroll records help streamline tax audits and labor inspections. Having clear documentation of hours worked, pay rates, and deductions allows companies to respond quickly to audit inquiries, minimizing disruptions and reducing the risk of additional penalties.
- Dispute Resolution: Payroll disputes and wage claims can arise unexpectedly. With detailed, up-to-date records, including overtime logs and deduction authorizations, employers have objective evidence to resolve disagreements fairly and efficiently. This not only prevents costly legal settlements but also protects both employer and employee rights.
- Financial Accuracy: Accurate payroll records reduce errors in employee compensation, ensuring workers are paid correctly and on time. This accuracy also helps maintain employee satisfaction and reduces administrative costs associated with correcting payroll mistakes.
- Employee Trust: When employees receive clear payslips and can see exactly how their compensation is calculated, it builds a culture of trust. This commitment to clarity strengthens employee relationships and positions your company as a fair and reliable employer.
- Operational Efficiency: Detailed payroll records help businesses accurately track payroll costs, labor expenses, and staffing needs. By analyzing these costs, organizations can improve budgeting, reduce unnecessary expenses, and allocate resources more effectively, leading to smoother and more cost-efficient operations.
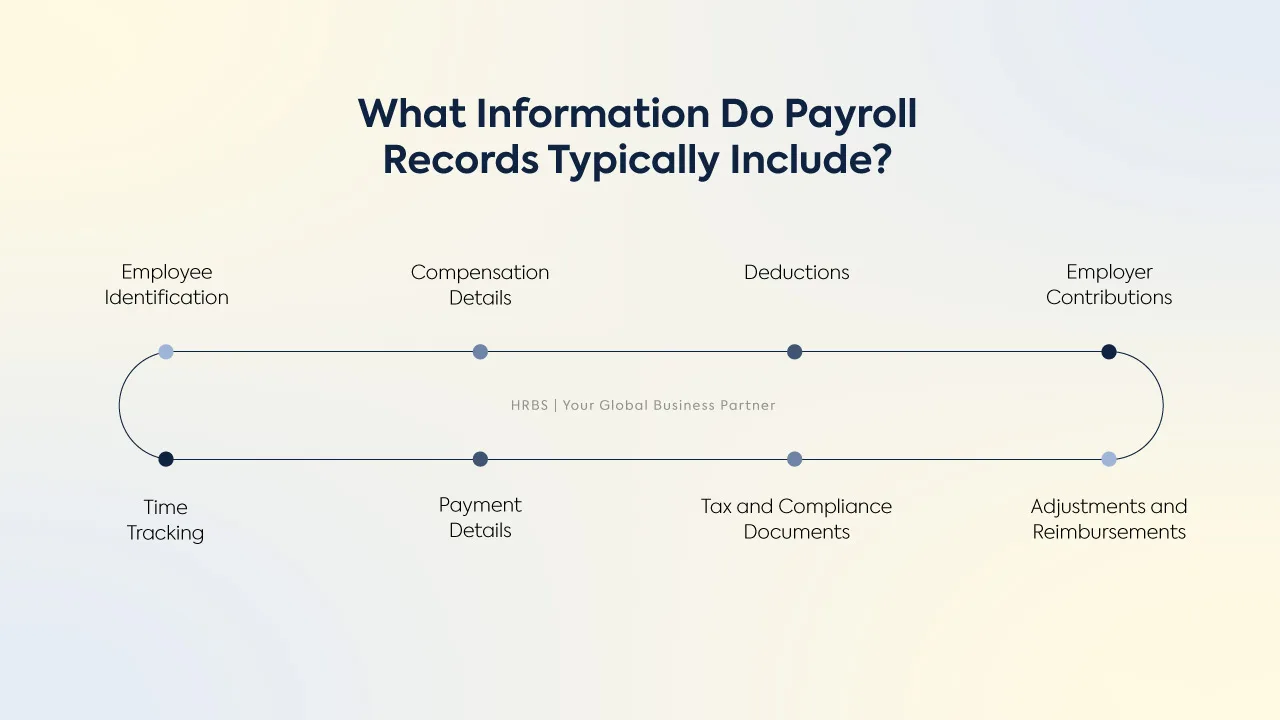
What Information do Payroll Records Typically Include?
Payroll records are comprehensive and must capture a wide range of information to serve their multiple purposes effectively. The typical payroll record contents include:
- Employee Identification: This includes the employee’s full name, unique employee identification number, job title, department, CNIC number, employment location, and employment start and end dates when applicable. Including employment tenure details supports workforce planning and legal compliance.
- Pay Information: Payroll records must detail gross salary or wages before deductions, net pay after deductions, payment frequency (monthly, bi-weekly), bonuses, commissions, overtime payments, allowances, and any other form of remuneration such as incentives or special compensations.
- Deductions: These include all mandatory taxes withheld at federal, state, and local levels, along with voluntary deductions such as health insurance premiums, retirement plan contributions, union dues, wage garnishments, and other benefit-related deductions. Recording these precisely ensures compliance and helps employees understand how their pay is calculated.
- Employer Contributions: Track employer-side contributions for social security schemes, employee provident fund, EOBI contributions, health and welfare funds, pension schemes, and other mandatory benefits. This data supports statutory reporting and benefits administration.
- Time Tracking: Accurate records of hours worked—regular, overtime, paid leave (like vacation and sick time), and unpaid leave—are essential to calculating wages correctly and complying with local labor laws. The timekeeping data should be detailed enough to support payroll calculations and handle any disputes over work hours.
- Payment Details: Payroll records should clearly state the pay period start and end dates, the date payment was made, and the method of payment (such as direct deposit, check, or cash). This information helps maintain transparency with employees and simplifies internal tracking and external audits.
- Tax and Compliance Documentation: To meet tax and labor law requirements, payroll records must include supporting documents like payroll tax filings, signed authorization forms, and certifications of compliance. Keeping these on file shows readiness for reviews by tax authorities or labor departments.
- Adjustments and Reimbursements: Any payroll corrections, such as retroactive pay adjustments, error corrections, or reimbursements for business-related expenses, must be clearly recorded with detailed explanations and relevant authorization.
Payroll Records Retention: How Long to Keep them?
Maintaining accurate and compliant payroll records is a legal obligation as well as a best practice for effective financial management and audit readiness. The retention period for payroll records varies depending on the specific type of record and applicable regulations, but generally falls within a consistent timeframe to meet tax and labor law requirements.
- General Payroll Records: Retain detailed payroll documents such as employee information, salary, overtime, deductions, and social security contributions for a minimum of 5 to 7 years.
- Tax Documentation: Hold on to Income Tax Returns and related tax deduction documents for 6 years after the tax year ends. These are important in case of tax audits or questions.
- Employment Records: Maintain employment service records as required by laws like The Employment (Record of Services) Act, 1951, for the prescribed duration or longer wherever applicable.
- Payslips: Keep issued payslips, showing employee details, pay period, gross/net pay, and deductions, for at least 3 to 5 years. This supports audit inspections and employee reference requests.
- Additional Important Payroll Documents: Also retain record summaries of statutory contributions (e.g., social security, pension, employee insurance) and loan or advance repayments for the same retention periods to maintain comprehensive payroll history and support statutory compliance.
Disposal of Records: After the retention period, securely dispose of payroll records containing sensitive employee information to protect privacy and comply with data protection regulations. Follow best practices such as shredding physical documents and permanently deleting digital files.
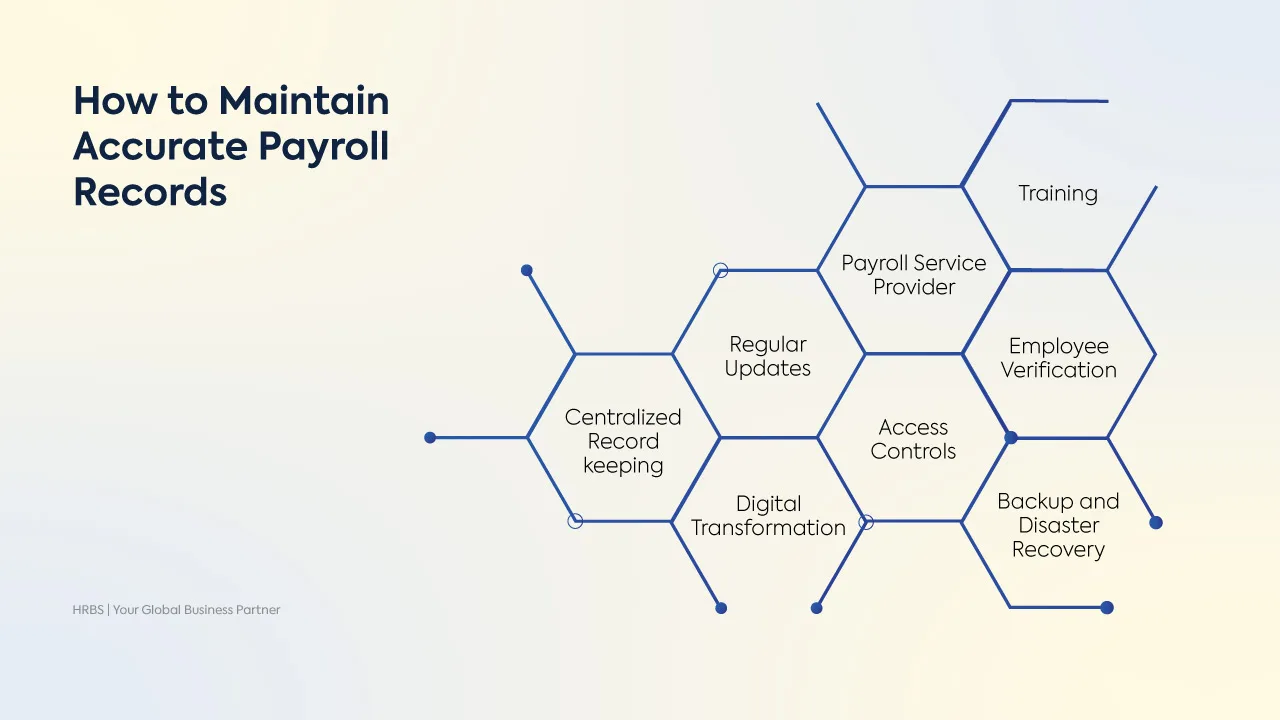
Best Practices to Maintain Accurate Payroll Records
Maintaining accurate payroll records is essential not only for compliance but also for smooth business operations, building employee trust, and avoiding costly payroll errors and penalties. By following key steps to keep your payroll data reliable, secure, and up to date, you can minimize mistakes that lead to incorrect payments and regulatory issues, ensuring accuracy and confidence throughout your payroll process.
- Organize Payroll Data:Keep all payroll information- employee details, salaries, deductions, overtime, and leave within a single, organized system. Use software or databases that support audit trails and version control to track changes over time, improving transparency and accountability.
- Use Reliable Payroll Software: Choose payroll software that not only automates salary computations, tax deductions, statutory compliance, and payslip generation but also offers integrated employee self-service portals, customizable reports, and multi-jurisdiction tax support.
- Keep Employee Data Updated: Regularly update employee information including tax status, identification numbers, bank details, and employment changes by implementing automated reminders and workflows that trigger document verification at key tax or employment milestones.
- Perform Regular Payroll Audits: Conduct comprehensive payroll audits that include cross-checking with attendance records, tax filings, social security contributions, and employee contracts. Use analytics tools as well to identify unusual payroll patterns such as duplicate payments or unexplained deductions.
- Secure Payroll Data:Implement multi-layer security measures such as role-based access control, end-to-end encryption, and multi-factor authentication to safeguard payroll data. Regularly conduct security risk assessments and staff awareness programs to prevent data breaches.
Train Payroll Staff: Beyond initial training, create a continuous professional development program including updates on evolving tax regulations, software training workshops, and scenario-based compliance exercises. Encourage certification in payroll management and participation in industry forums or webinars.
Common Payroll Record Challenges
Managing payroll records accurately and efficiently is essential for any business, but it comes with several common challenges that can impact compliance, employee satisfaction, and financial accuracy. Here are key payroll records challenges businesses often face, along with insights on why they matter:
- Data Entry Errors: Inaccurate or incomplete payroll data such as wrong employee details, salary figures, or tax information lead to calculation mistakes. These errors can result in incorrect paychecks, delayed payments, tax filing problems, and costly corrections. Beyond financial impact, data errors reduce employee confidence and increase the risk of regulatory audits.
- Regulatory Changes: Tax laws, labor regulations, and statutory obligations change regularly. Failing to adjust payroll processes in line with new rules leads to improper tax withholdings, missed filings, and penalties. Keeping payroll compliant requires continuous updates and monitoring, which can be challenging without the right expertise or tools.
- Delays in Updating Employee Information: Employee details such as bank accounts, tax exemptions, job roles, and employment status directly impact payroll cost calculations. When these changes are not captured immediately, it causes payment inaccuracies and reporting errors, potentially resulting in employee dissatisfaction or legal issues.
- Lack of System Integration: Many companies struggle with disconnected payroll, HR, accounting, and tax systems. Without seamless integration, data must be manually transferred between platforms. This redundant effort increases the chance of errors, wastes valuable time, and complicates end-of-year audits or compliance reviews.
- Poor Record Organization: Unorganized or incomplete payroll records make it hard to find needed information during audits or dispute resolution. Misplaced or missing documents can also lead to compliance violations, regulatory fines, and damage to your organization’s reliability and employee trust.
Benefits of Accurate Payroll Records
Accurate payroll records are critical for running a compliant and efficient business. They not only help meet legal obligations but also improve financial management, employee relations, and operational transparency.
- Legal Compliance: Keeping detailed payroll records allows your business to meet all tax and labor law requirements without gaps. Clear documentation of wage payments, tax withholdings, and statutory contributions protects you from fines, audits, and legal action. This compliance is crucial for maintaining your company’s reputation and financial health.
- Cost Control: Complete payroll data provides real-time visibility into salary expenses, bonuses, overtime, and deductions. This accurate information helps managers plan budgets effectively, spot unusual payroll costs early, and make informed decisions to optimize labor spending.
- Faster Payroll Processing: Well-maintained payroll records streamline paycheck calculations and reduce manual errors. This leads to faster payroll runs, fewer payment mistakes, and ensures employees receive the correct pay on time, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming corrections.
- Employee Transparency: Transparent payroll documentation allows employees to clearly understand their earnings, deductions, and benefits. When employees can easily verify their pay, it builds trust, lowers payroll-related queries, and positively impacts workplace morale and retention.
- Audit Readiness: Comprehensive payroll records create a clear audit trail, facilitating smoother inspections by tax authorities and internal audits. These records help resolve disputes quickly, provide strong evidence against payroll fraud or wage claims, and reduce business risks linked to payroll compliance issues.
Technology’s Role in Streamlining Payroll Records
Managing payroll records manually is no longer practical, especially as payroll complexities grow with changing tax laws, diverse employee types, and strict data privacy rules. Technology has become essential for creating efficient, compliant, and scalable payroll operations.
- Automation: Modern payroll software automates the entire payroll records process, from capturing and storing data to securing and reporting it. This automation reduces the risk of human error and ensures that accurate payroll records are available in real time for compliance, audits, and management reviews.
- Real-Time Data: Leading payroll platforms automatically gather all relevant data during each pay cycle, including time tracking, deductions, tax filings, benefits, and employer contributions. This real-time capture ensures reliable, clean data that supports timely reporting and decision-making without guesswork.
- Payroll Records Across Teams: Centralized payroll systems remove silos by providing a single source of truth accessible to HR, finance, and compliance teams across multiple locations. This unified access helps faster audits, consistent record templates, improved tracking of retention timelines, and better reconciliation between payroll, accounting, and HR systems
- Integration Capabilities: To maintain data accuracy across the employee lifecycle, payroll technology integrates with systems such as HRIS platforms, time-tracking tools, expense management software, and compliance/reporting applications. These integrations remove manual entries and data duplication, keeping payroll records aligned with actual employee data and organizational compliance needs.
- Improved Error Detection: Modern payroll systems include built-in validation checks and alerts that automatically identify inconsistencies, missing data, or potential errors before payroll is finalized. These early warnings help payroll teams fix issues quickly, reducing costly mistakes, minimizing payment delays, and ensuring compliance with tax and labor laws.
Payroll Records Audits: What to Expect
Payroll audits are formal reviews carried out by tax authorities or labor departments to verify that businesses follow payroll laws and regulations. Proper preparation and understanding of the audit process can reduce risk and disruptions.
- Document Requests: Auditors will ask for payroll registers, time and attendance records, tax filings, payment confirmations, and deduction authorizations.
- Verification of Accuracy: Auditors compare wages paid to recorded hours worked, ensuring correct pay rates and overtime calculations. They also verify tax withholdings and employer contributions are accurate and timely.
- Compliance Checks: Auditors check compliance with labor laws covering minimum wage, overtime rules, record retention policies, and other legal requirements.
- Discrepancy Resolution: Be prepared to explain any anomalies or errors found during the audit.
- Potential Penalties: Non-compliance can cause fines, interest on unpaid taxes, and legal action.
How to Prepare Effectively For Payroll Audit
- Organize payroll records ahead of time to facilitate quick access.
- Conduct internal audits regularly to catch issues early.
- Keep up-to-date with all legal requirements and payroll changes.
- Train staff responsible for payroll on compliance and documentation best practices.
How HRBS Can Help with Payroll Record Keeping?
Managing payroll records can be complex and time-consuming, especially for businesses aiming to stay compliant and efficient. HRBS simplifies the process by offering expert payroll outsourcing services, proven processes, and continuous compliance support. Here’s how HRBS delivers clear value and builds industry-leading authority in payroll record management:
- Complete Compliance Management: HRBS ensures payroll records fully follow the latest labor laws and tax regulations, including recent changes to Pakistan’s employment rules. This careful approach reduces risks of fines, penalties, and legal issues, helping businesses avoid costly disruptions.
- Strong Data Security: Understanding the sensitive nature of payroll data, HRBS uses strict data protection methods such as encryption, secure storage, and controlled access. This focus lowers data breach risks and follows global best practices for employee privacy.
- Payroll Process Outsourcing: By handling payroll management, HRBS saves businesses time and resources, allowing staff to focus on core work without worrying about payroll details. This improves accuracy and timeliness of payroll delivery, lowering employee concerns and compliance risks.
- Scalable and Cost-Effective Solutions: Whether a growing startup or a multinational enterprise, HRBS offers payroll and EOR services tailored to diverse business needs, covering multi-location operations, various employment types, and evolving workforce demands with flexible, cost-efficient packages.
- Accurate and Transparent Records: Detailed, well-organized payroll documentation supported by clear audit trails allows quick and thorough internal reviews, simplifies reporting, and ensures readiness for government audits.
Discover how HRBS can simplify your payroll management, start your journey with us today.
FAQs
What are Payroll Records and why they are important?
Payroll records, also known as payroll documentation, are official documents that contain detailed information about employee compensation. These include employee personal details, salary amounts, hours worked, tax withholdings, benefit and social security contributions, bonuses, deductions, payment history, and compliance filings. Payroll records ensure accurate payments, help companies stay compliant with labor and tax laws, and provide critical evidence during audits or payroll disputes.
How long should payroll records be kept?
Payroll records should be retained for 5 to 7 years to comply with tax authorities and labor laws, though specific types of documents have varying retention requirements. For instance, tax-related documentation such as income tax returns and withholding certificates should be kept for at least 6 years after the fiscal year ends, while payslips are generally retained for 3 to 5 years. Adhering to these retention periods supports audit readiness, regulatory compliance, and effective record management.
What happens if payroll records are lost?
Losing payroll records can cause severe operational and legal problems, including difficulties verifying employee payments, delays in tax submissions, and increased risks during audits. It can lead to penalties for non-compliance with statutory record-keeping laws, disputes with employees, and damaged business reputation. To avoid these risks, businesses should implement regular data backups, use secure digital storage with encryption, and maintain a clear payroll records retention policy.
Can employees access their payroll records?
Yes, employees generally have the right to access their payroll records to review their earnings, tax deductions, benefits, and payment history. Providing easy access, often through employee self-service portals or upon request improves payroll transparency and helps resolve discrepancies quickly. This access supports trust between employers and employees and is often mandated by labor laws.
What are the penalties for not maintaining proper payroll records?
Failure to maintain accurate and complete payroll records can result in legal penalties, including fines, interest charges on unpaid taxes, and potential legal action by labor or tax authorities. Any person who fails to maintain the required payroll records shall be liable to pay a penalty of ten thousand rupees or five percent of the amount of tax on income, whichever is higher. This penalty underscores the importance of maintaining proper payroll documentation to avoid financial sanctions. Beyond fines, poor record-keeping increases the risk of audit issues, payroll errors, employee disputes, and compliance failures, which can disrupt operations and harm business reputation.